Charge
Density Studies of Weak Interactions in Organic Solids
Krzysztof WoŸniak, Paul Mallinson, Paulina M. Dominiak
Department of
Chemistry, The University of Warsaw, Pasteura 1, 02 093 Warszawa, Poland.
E-mail: kwozniak@chem.uw.edu.pl
Experimental charge density distributions
in a series of ionic complexes of 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene (DMAN) with four different acids:
1,2,4,5-benzenetetracarboxylic acid (pyromellitic acid), 4,5-dichlorophthalic acid, dicyanoimidazole,
and o-benzoic sulfimide dihydrate (saccharin) proved that all the interactions
studied {[O…H…O]-,
C-H…O, [N-H…N]+, O-H…O, C-H…N, Cp…Np,
Cp…Cp,
C-H…Cl, N-H+} follow exponential dependences of the electron density, local kinetic and
potential energies at the bond critical points on the length of the interaction
line1,2. The local potential
energy density at the bond critical points has a near-linear relationship to
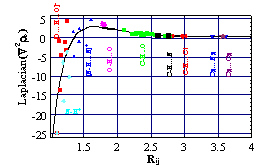
the electron density. There is also a Morse-like dependence of the laplacian of rho on the length of interaction
line, which allows a differentiation of ionic and covalent bond characters. The
strength of the interactions studied varies systematically with the relative
penetration of the critical points into the van der Waals spheres of the donor and
acceptor atoms, as well as on the interpenetration of the van der Waals spheres
themselves. We hope to extend the results using some more data regarding a
series of Schiff bases.
![Pole tekstowe: Figure 1. Morse type dependence of Ñ2rb [eÅ-5] on the length of interaction line [Å]: Ñ2rb = 3(1)-3(2){1-exp[-2.3(6)(Rij - 1.66(8))]}2, curvilinear correlation coefficient R= 0.78 for N = 63 datapoints.](./Krzysztof%20Wozniak_pliki/image001.gif)
(1) Mallinson, P. R.; Smith, G. T.; Wilson, C. C.;
Grech, E.; Wozniak, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, pp.
4259-4270.
(2) Wozniak, K.; Mallinson, P. R.; Smith, G. T.;
Wilson, C. C.; Grech, E. J. Phys. Org. Chem. Chem., 2003, 16(10),
pp. 764-771.